You Need to Know About All Cashew Grades & Kernels
All You Need to Know About Cashew Grades & Cashew Kernels
Cashew is a highly nutritious and concentrated form of food, providing a substantial amount of energy. The cashew nut kernel has a pleasant taste and flavor and can be eaten raw, fried and sometimes salted or sweetened with sugar. It also contributes as an important source of invisible fat in the diet, being widely used in a variety of ways. There has been a growing demand for cashew in many temperate countries where the demand is increasing. The nut contains an acrid compound which is a powerful vesicant that is abrasive to the skin. The cashew shell contains 25% of this reddish brown oil, industrially known as Cashew Nut Shell Liquid (CNSL) which is a by-product of the roasting process.
Types of Cashew grades
Cashew grades refer to the classification of cashew nuts based on their size, shape, color, and quality. The grading system helps determine the value and marketability of cashew nuts. Here is some information about cashew grades:
- Whole Cashews: Whole cashews are the highest grade and most desirable. They have a uniform shape, size, and color. Whole cashews are often used for snacking or as an ingredient in various dishes.
- Split Cashews: Split cashews are whole cashews that have been manually or mechanically split into two halves. They are commonly used in cooking and baking.
- Broken Cashews: Broken cashews are cashew nuts that have broken into smaller pieces during processing. They are often used in the food industry for making cashew butter, cashew milk, or as an ingredient in confectionery products.
- Scorched Cashews: Scorched cashews have a slightly darker color due to over-roasting during processing. They may have a slightly different flavor compared to regular cashews.
- Dessert Cashews: Dessert cashews are cashews that have been roasted with sugar or other sweeteners. They have a sweet and crunchy taste and are often used in desserts or as a topping for ice cream.
- Cashews Pieces: Cashew pieces refer to small fragments or irregularly shaped cashew nuts. They are often used in cooking, baking, or as an ingredient in snack mixes.
- Cashew Meal: Cashew meal is made by grinding cashew kernels into a fine powder. It is commonly used as a gluten-free alternative to flour in baking or as a thickening agent in sauces and soups.
- Roasted Cashews: Roasted cashews are cashew kernels that have been roasted to enhance their flavor. They are often eaten as a snack or used in cooking and baking.
It's important to note that different countries and regions may have their own grading systems for cashews. Additionally, the quality and grading standards can vary among different suppliers and manufacturers. When purchasing cashews, it's advisable to check the grading information provided by the seller to ensure you are getting the desired quality and grade.
What is Cashew Kernels?
Cashew kernels are the edible seeds of the cashew tree, scientifically known as Anacardium occidentale. They are commonly used in cooking and baking, as well as eaten as a snack on their own. Cashew kernels have a rich, buttery flavor and a creamy texture. They are often used in various cuisines, including Indian, Thai, and Mediterranean dishes. Cashew kernels are also a good source of healthy fats, protein, vitamins, and minerals.
Different grades of Cashew kernels based on their size and quality
Cashew kernels are graded based on their size and quality. The grading system varies slightly depending on the country of origin, but generally, the following grades are commonly used:
- W180 Cashews: This grade represents the largest cashew kernels. "W" stands for "white," indicating the color of the kernel. The number "180" refers to the number of kernels per pound (approximately 454 grams). W180 cashews are considered premium quality and are often used for gourmet purposes.
- W210 Cashews: These cashew kernels are slightly smaller than W180, with approximately 210 kernels per pound. They are also of high quality and are commonly used in various culinary applications.
- W240 Cashews: This grade represents cashew kernels with approximately 240 kernels per pound. W240 cashews are widely used in cooking, baking, and snacking. They are considered a versatile grade suitable for most applications.
- W320 Cashews: These cashew kernels have approximately 320 kernels per pound. W320 cashews are commonly used in cooking, baking, and snacking. They are slightly smaller than W240 but still of good quality.
- W450 Cashews: This grade represents cashew kernels with approximately 450 kernels per pound. W450 cashews are smaller in size and are often used in confectionery, chocolate, and as toppings for desserts.
- SW Cashews: SW stands for "scorched wholes." These cashew kernels have a slightly darker color due to the roasting process. They are available in various sizes, such as SW180, SW210, SW240, etc., and are commonly used in cooking, baking, and snacking.
- Splits Cashews: Cashew splits are cashew kernels that have been split into two or more pieces. They are often used in cooking, baking, and as toppings for various dishes.

W150
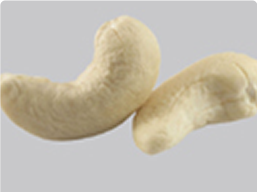
W180

W240

W320

W400
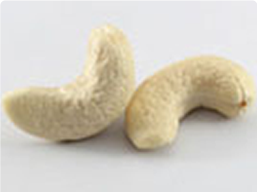
A210

A240

A320

300

WW

SW

ASW

SSW

DW
Cashews Pieces

JH

S

DS

JB
JK

K

LWP

SP

P

DP

SWP

SDP

BB
Health benefits of Cashews
Cashews are not only delicious but also offer several health benefits. Here are some of the key health benefits of cashews:
- Heart health: Cashews are rich in monounsaturated fats, which are considered heart-healthy fats. These fats help lower bad cholesterol levels (LDL) and increase good cholesterol levels (HDL), reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Nutrient-rich: Cashews are packed with essential nutrients such as vitamins (vitamin E, vitamin K, and B vitamins), minerals (copper, magnesium, zinc, and phosphorus), and antioxidants. These nutrients support overall health and contribute to various bodily functions.
- Weight management: Despite being calorie-dense, cashews can aid in weight management. The combination of healthy fats, protein, and fiber in cashews helps promote satiety, keeping you feeling full for longer and reducing overeating.
- Bone health: Cashews contain minerals like magnesium, copper, and phosphorus, which are essential for maintaining strong and healthy bones. These minerals contribute to bone density and help prevent conditions like osteoporosis.
- Blood sugar control: Cashews have a low glycemic index, meaning they cause a slower rise in blood sugar levels compared to high-glycemic foods. This makes them a suitable snack option for individuals with diabetes or those looking to manage blood sugar levels.
- Eye health: Cashews are a good source of antioxidants like lutein and zeaxanthin, which are beneficial for eye health. These antioxidants help protect the eyes from damage caused by harmful free radicals and may reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration.
- Improved digestion: Cashews contain dietary fiber, which aids in digestion and prevents constipation. Fiber also promotes a healthy gut microbiome, supporting overall digestive health.
- Reduced inflammation: Cashews contain compounds like polyphenols and antioxidants that possess anti-inflammatory properties. Regular consumption of cashews may help reduce inflammation in the body and lower the risk of chronic diseases associated with inflammation.
It's important to note that while cashews offer numerous health benefits, they are also high in calories. Therefore, it's essential to consume them in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
Health benefits of Cashews for Men
Cashews offer several health benefits specifically for men . Here are some of the key health benefits of cashews for men:
- Prostate health: Cashews are rich in zinc, a mineral that plays a crucial role in maintaining prostate health. Adequate zinc intake has been associated with a reduced risk of prostate issues, including enlargement and cancer.
- Testosterone production: Zinc is also essential for testosterone production in men. Testosterone is a hormone that plays a vital role in male reproductive health, muscle growth, bone density, and overall well-being. Cashews' high zinc content can support healthy testosterone levels.
- Heart health: Heart disease is a significant concern for men. Cashews contain monounsaturated fats, which can help lower bad cholesterol levels (LDL) and increase good cholesterol levels (HDL). This can reduce the risk of heart disease and promote cardiovascular health.
- Muscle growth and recovery: Cashews are a good source of protein, which is essential for muscle growth and repair. Adequate protein intake is crucial for men who engage in regular exercise or strength training to support muscle development and recovery.
- Energy and stamina: Cashews are a rich source of vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats, providing a good energy boost. The combination of protein, healthy fats, and carbohydrates in cashews can help improve stamina and endurance, making them a great snack option for active men.
- Bone health: Cashews contain minerals like magnesium and phosphorus, which are essential for maintaining strong and healthy bones. These minerals contribute to bone density and can help prevent conditions like osteoporosis.
- Mental health: Cashews contain nutrients like magnesium and vitamin B6, which are important for brain health and mood regulation. Adequate intake of these nutrients can support cognitive function and help reduce the risk of mental health issues such as depression and anxiety.
It's important to note that while cashews offer numerous health benefits for men, they should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. Additionally, individual health conditions and dietary needs may vary, so it's always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Health benefits of Cashews for Women/Girl
Cashews offer several health benefits for women/girls . Some of these benefits include:
- Heart health: Cashews are rich in monounsaturated fats, which are considered heart-healthy fats. These fats help to lower bad cholesterol levels (LDL) and increase good cholesterol levels (HDL), reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Bone health: Cashews are a good source of minerals like calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus, which are essential for maintaining strong and healthy bones. Regular consumption of cashews can help prevent conditions like osteoporosis and reduce the risk of fractures.
- Weight management: Cashews are relatively low in calories and high in fiber, making them a satisfying snack that can help with weight management. The fiber content also aids in digestion and prevents constipation.
- Antioxidant properties: Cashews contain antioxidants like vitamin E, which help to neutralize harmful free radicals in the body. These antioxidants can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases, including certain types of cancer.
- Improved brain function: Cashews are a good source of nutrients like magnesium, iron, and zinc, which are essential for brain health. These nutrients support cognitive function, memory, and overall brain health.
- Hormonal balance: Cashews contain phytoestrogens, which are plant compounds that mimic the effects of estrogen in the body. These compounds can help regulate hormonal imbalances in women, particularly during menopause.
- Skin health: Cashews are rich in antioxidants and healthy fats, which can help improve skin health. The antioxidants protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals, while the healthy fats help maintain moisture and elasticity, reducing the signs of aging.
It's important to note that while cashews offer numerous health benefits, they should be consumed in moderation as they are high in calories. Additionally, individuals with nut allergies should avoid cashews.
Cashews: Nutrition Value in 28g
| Moisture | 5.9 |
| Total Minerals | 2.4 |
| Total Fiber | 1.3 |
| Energy | 785 |
| Protein | 24 |
| Total Fat | 64 |
| Saturated | 12.9 |
| Unsaturated (Oleic) | 36.8 |
| Unsaturated (Linoleic) | 10.2 |
| Carbohydrate | 41 |
| Ca | 53 |
| P | 52.2 |
| Fe | 5.3 |
| Thiamin | 0.63 |
| Riboflavin | 0.19 |
| Niacin | 2.5 |
| Beta-carotene | 60 |
| Retinol Equivalent | 33 IU; 10 mcg |
| Vitamin K | 650 |
Cashews: Protein Content
| Amino Acid | Composition (%) |
| Glutamic Acid | 28.0 |
| Leucine | 11.93 |
| Iso Leucine | 3.86 |
| Alanine | 3.18 |
| Phenylalanine | 4.35 |
| Tyrosine | 3.20 |
| Arginine | 10.30 |
| Glycine | 5.33 |
| Histidine | 1.81 |
| Lysine | 3.32 |
| Methionine | 1.30 |
| Cystine | 1.02 |
| Threonine | 2.78 |
| Valine | 4.53 |
| Tryptophane | 1.37 |
| Aspartic Acid | 10.78 |
| Proline | 3.72 |
| Serine | 5.76 |
Wide differences in the protein content ranging from 13.13 to 25.03% have been reported from various regions of India. It has been suggested that protein content be considered as one of the most important factors in future breeding and selection programs on Cashew nut.
Cashews: Mineral Content
| Ca | 0.04 |
| P | 0.88 |
| Na | 0.005 |
| K | 0.57 |
| Mg | 0.28 |
| Fe | 0.008 |
| Cu | 0.002 |
| Zn | 0.004 |
| Mn | 0.002 |
Cashews: Vitamin Content (mg per 100 gm) of Cashew Kernels
The vitamin content of cashew nut kernels that 0.5 to 1.4 mg per 100 g of thiamin and 0.58 mg per 100 g of riboflavin, a good proportion of vitamin E and traces of other vitamins are present in cashew.
| Thiamin | 0.56 |
| Niacin | 3.68 |
| Riboflavin | 0.58 |
| Tocopherol | 210 |
| Pyridoxine | traces |
| Axerophtol | traces |
| Vitamin D | traces |
Cashews: Fatty Acid Composition of Cashew Kernels (%)
The fat and oil content of cashew nut contributes substantially to its energy content and consists mostly of glycerides of oleic acid (73.8%) and linoleic acids (7.7%).
| Oleic Acid | 73.3 |
| Linoleic Acid | 7.67 |
| Palmitic Acid | 0.89 |
| Stearic Acid | 11.24 |
| Lignoseric Acid | 0.15 |
| Unsaponifiable Matter | 0.42 |
Cashews: Carbohydrate Content
Analysis of cashew nut kernels from different regions of India have revealed that there are variations in the reducing sugar content from 1% to 3% and the non-reducing sugars from 2.4% to 8.7%. Starch content ranged from 4.6% to 11.2% and the oil content also showed a wide variability from 34.5% to 46.8%.
Recent posts
Contact Us
If you have any inquiries or feedback, please don't hesitate to reach out to us at [email protected]. We will respond to your request as soon as possible. Thank you very much for your interest!
Country profiles
- Afghanistan
- Aland Islands
- Albania
- Algeria
- American Samoa
- Andorra
- Angola
- Anguilla
- Antarctica
- Antigua And Barbuda
- Argentina
- Armenia
- Aruba
- Australia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- The Bahamas
- Bahrain
- Bangladesh
- Barbados
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Belize
- Benin
- Bermuda
- Bhutan
- Bolivia
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Botswana
- Bouvet Island
- Brazil
- British Indian Ocean Territory
- Brunei
- Bulgaria
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cambodia
- Cameroon
- Canada
- Cape Verde
- Cayman Islands
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Chile
- China
- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Colombia
- Comoros
- Congo
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Cook Islands
- Costa Rica
- Cote D'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Croatia
- Cuba
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Djibouti
- Dominica
- Dominican Republic
- East Timor
- Ecuador
- Egypt
- El Salvador
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Estonia
- Ethiopia
- Falkland Islands
- Faroe Islands
- Fiji Islands
- Finland
- France
- French Guiana
- French Polynesia
- French Southern Territories
- Gabon
- Gambia The
- Georgia
- Germany
- Ghana
- Gibraltar
- Greece
- Greenland
- Grenada
- Guadeloupe
- Guam
- Guatemala
- Guernsey and Alderney
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Guyana
- Haiti
- Heard Island and McDonald Islands
- Honduras
- Hong Kong S.A.R.
- Hungary
- Iceland
- India
- Indonesia
- Iran
- Iraq
- Ireland
- Israel
- Italy
- Jamaica
- Japan
- Jersey
- Jordan
- Kazakhstan
- Kenya
- Kiribati
- North Korea
- South Korea
- Kuwait
- Kyrgyzstan
- Laos
- Latvia
- Lebanon
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macau S.A.R.
- North Macedonia
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Malaysia
- Maldives
- Mali
- Malta
- Man (Isle of)
- Marshall Islands
- Martinique
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Mayotte
- Mexico
- Micronesia
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Mongolia
- Montenegro
- Montserrat
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Myanmar
- Namibia
- Nauru
- Nepal
- Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba
- Netherlands
- New Caledonia
- New Zealand
- Nicaragua
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Niue
- Norfolk Island
- Northern Mariana Islands
- Norway
- Oman
- Pakistan
- Palau
- Palestinian Territory Occupied
- Panama
- Papua new Guinea
- Paraguay
- Peru
- Philippines
- Pitcairn Island
- Poland
- Portugal
- Puerto Rico
- Qatar
- Reunion
- Romania
- Russia
- Rwanda
- Saint Helena
- Saint Kitts And Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Saint Vincent And The Grenadines
- Saint-Barthelemy
- Saint-Martin (French part)
- Samoa
- San Marino
- Sao Tome and Principe
- Saudi Arabia
- Senegal
- Serbia
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Singapore
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Solomon Islands
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Georgia
- South Sudan
- Spain
- Sri Lanka
- Sudan
- Suriname
- Svalbard And Jan Mayen Islands
- Swaziland
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Syria
- Taiwan
- Tajikistan
- Tanzania
- Thailand
- Togo
- Tokelau
- Tonga
- Trinidad And Tobago
- Tunisia
- Turkey
- Turkmenistan
- Turks And Caicos Islands
- Tuvalu
- Uganda
- Ukraine
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- United States of America
- United States Minor Outlying Islands
- Uruguay
- Uzbekistan
- Vanuatu
- Vatican City State (Holy See)
- Venezuela
- Vietnam
- Virgin Islands (British)
- Virgin Islands (US)
- Wallis And Futuna Islands
- Western Sahara
- Yemen
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
- Kosovo
- Curaçao
- Sint Maarten (Dutch part)